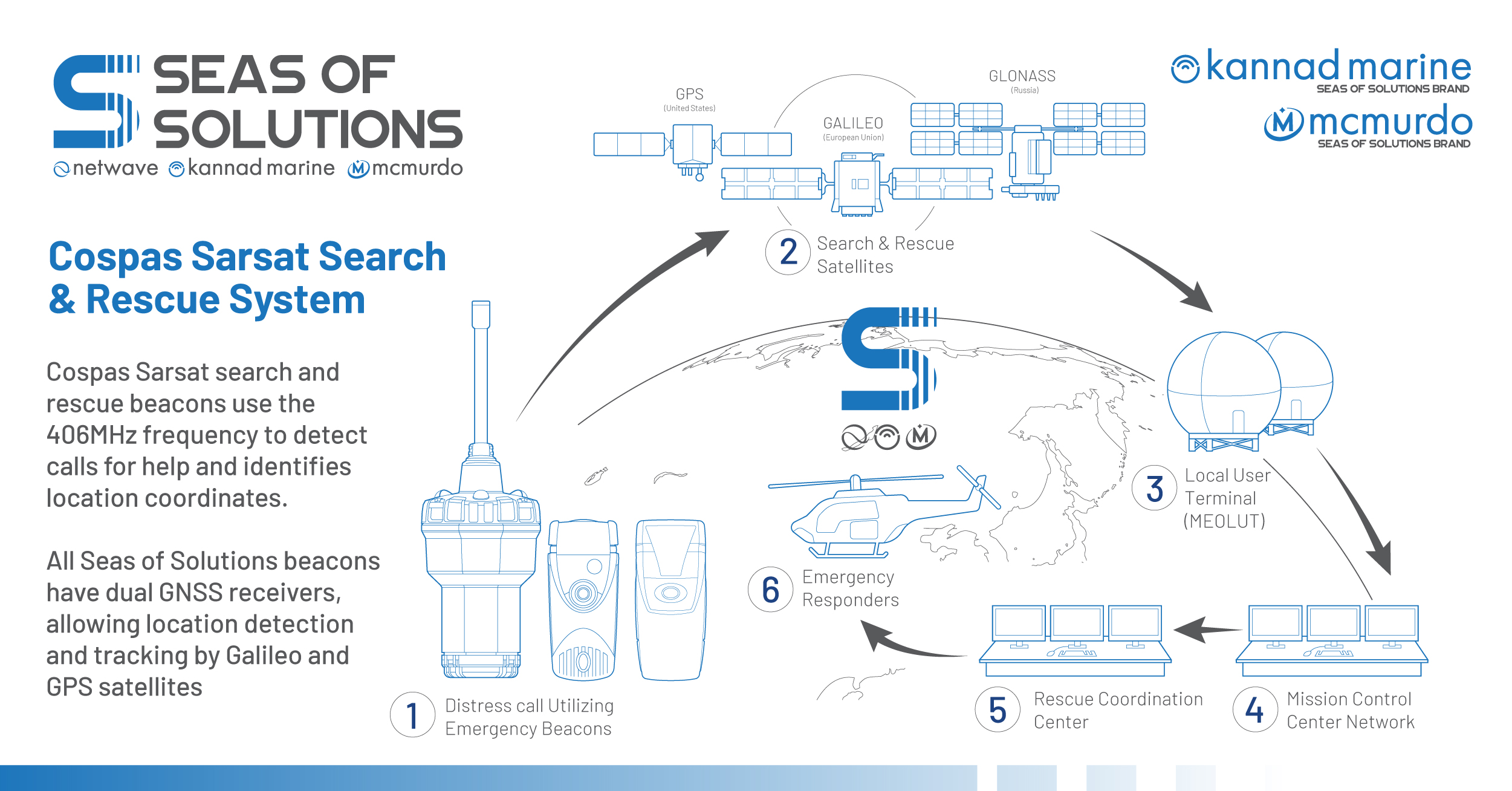
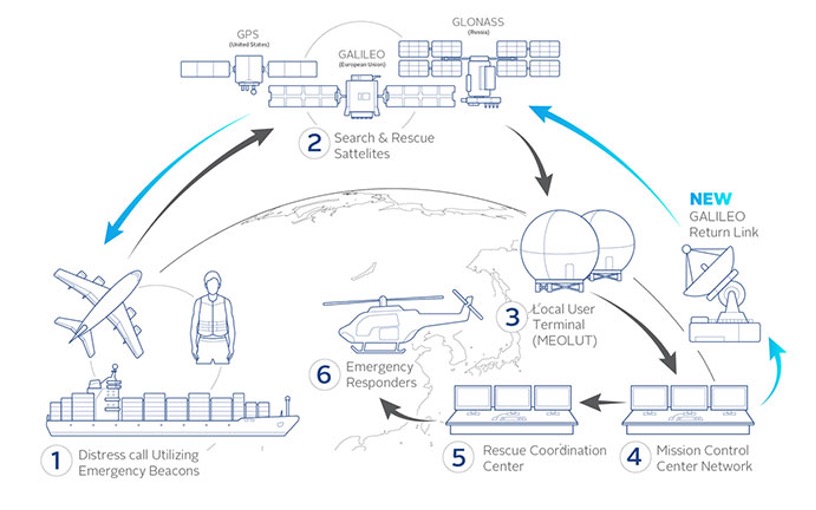
Galileo is the European Union’s Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) constellation, which reached its operational phase in 2017, allowing technology with a Galileo-enabled receiver to use signals provided by Galileo’s global satellite constellation for positioning, navigation and timing.
Galileo’s development is part of the EU’s preparations for upgrading the international distress beacon locating organisation COSPAS SARSAT’s Search and Rescue (SAR) Ecosystem under the MEOSAR program, which requires new earth based antenna and a network of 72 SAR satellites, made up of the US GPS, EU Galileo and Russian Glonass constellations.